|
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105 |
- # Sentinel Envoy RLS - Kubernetes sample
-
- This sample will illustrate how to use Sentinel RLS token server with Envoy in Kubernetes clusters.
-
- ## Build the Docker image
-
- We could use the pre-built Docker image: `registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/sentinel-docker-repo/sentinel-envoy-rls-server:latest`
-
- We can also manually build the Docker image in the `sentinel-cluster-server-envoy-rls` directory:
-
- ```bash
- docker build -t "sentinel/sentinel-envoy-rls-server:latest" -f ./Dockerfile .
- ```
-
- ## Deploy Sentinel RLS token server
-
- Next we could deploy the Sentinel RLS token server in the K8S cluster.
- We've provided a deployment template for Sentinel RLS token server in `sentinel-rls.yml`.
- It includes:
-
- - A `ConfigMap` that contains the cluster flow control rule for Envoy global rate limiting.
- This will be mounted as a file in the target `Deployment`, so that the Sentinel RLS token server
- could load the rules dynamically as soon as the rule in the `ConfigMap` has been updated.
- - A `Deployment` for Sentinel RLS token server. It will mount the `ConfigMap` as a volume
- for dynamic rule configuration.
- - A `Service` that exports the Sentinel command port (8719) and the RLS gRPC port (by default 10245)
- on a cluster-internal IP so that the Envoy pods could communicate with the RLS server.
-
- The sample rate limiting rule in the `sentinel-rule-cm`:
-
- ```yaml
- domain: foo
- descriptors:
- # For requests to the "service_httpbin" cluster, limit the max QPS to 1
- - resources:
- - key: "destination_cluster"
- value: "service_httpbin"
- count: 1
- ```
-
- You may enable the access log in the Sentinel RLS token server (output to console)
- via the `SENTINEL_RLS_ACCESS_LOG` env:
-
- ```yaml
- env:
- - name: SENTINEL_RLS_ACCESS_LOG
- value: "on"
- ```
-
- You may also append JVM opts via the `JAVA_OPTS` env.
-
- After preparing the yaml template, you may deploy the Sentinel RLS token server:
-
- ```bash
- kubectl apply -f sample/k8s/sentinel-rls.yml
- ```
-
- ## Deploy Envoy
-
- Next we could deploy the Envoy instances in the K8S cluster. If you've already had Envoy instances running,
- you could configure the address (`sentinel-rls-service`) and the port (`10245`)
- of the rate limit cluster in your Envoy configuration.
-
- We've provided a deployment template for Envoy in `envoy.yml`.
- It includes:
-
- - A `ConfigMap` that contains the configuration for Envoy.
- This will be mounted as a file in the target `Deployment`, which will be loaded as the configuration
- file by Envoy.
- - A `Deployment` for Envoy. It will mount the `ConfigMap` as a volume
- for configuration.
- - A `Service` that exports the Envoy endpoint port (by default 10000) on a cluster-internal IP
- so that it could be accessible from other pods. If you need external access, you could choose the
- `LoadBalancer` type or add a frontend ingress.
-
- In the sample, we have two [Envoy clusters](https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/api-v2/clusters/clusters):
-
- - `service_httpbin`: HTTP proxy to `httpbin.org`
- - `rate_limit_cluster`: the cluster of the Sentinel RLS token server
-
- This route configuration tells Envoy to route incoming requests to `httpbin.org`. In the `http_filters` conf item,
- we added the `envoy.rate_limit` filter to the filter chain so that the global rate limiting is enabled.
- We set the rate limit domain as `foo`, which matches the item in the Envoy RLS rule.
- In the `route_config`, we provide the rate limit action: `{destination_cluster: {}}`, which will
- generate the rate limit descriptor containing the actual target cluster name (e.g. `service_httpbin`).
- Then we could set rate limit rules for each target clusters.
-
- After preparing the yaml template, you may deploy the Envoy instance:
-
- ```bash
- kubectl apply -f sample/k8s/envoy.yml
- ```
-
- ## Test the rate limiting
-
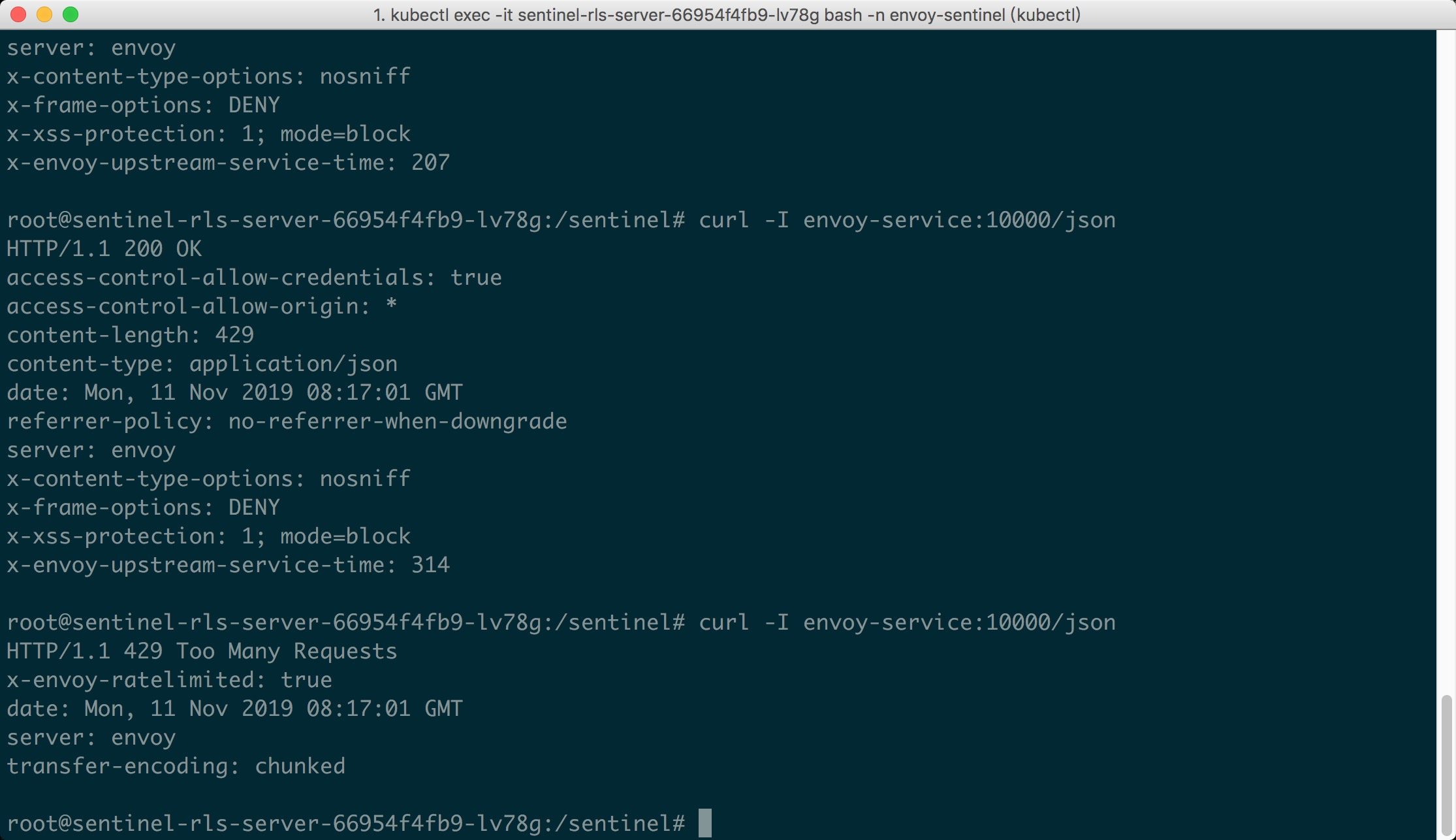
- Now it's show time! We could visit the URL `envoy-service:10000/json` in K8S pods.
- Since we set the max QPS to 1, we could emit concurrent requests to the URL, and we
- could see the first request passes, while the latter requests are blocked (status 429):
-
- 
-
- ## Update the rules dynamically
-
- You could update the rules in the `sentinel-rule-cm` ConfigMap. Once the content is updated,
- Sentinel will perceive the changes and load the new rules to `EnvoyRlsRuleManager`.
|
