|
|
vor 5 Jahren | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | vor 5 Jahren | |
| envoy.yml | vor 5 Jahren | |
| sentinel-rls.yml | vor 5 Jahren | |
README.md
Sentinel Envoy RLS - Kubernetes sample
This sample will illustrate how to use Sentinel RLS token server with Envoy in Kubernetes clusters.
Build the Docker image
We could use the pre-built Docker image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/sentinel-docker-repo/sentinel-envoy-rls-server:latest
We can also manually build the Docker image in the sentinel-cluster-server-envoy-rls directory:
docker build -t "sentinel/sentinel-envoy-rls-server:latest" -f ./Dockerfile .
Deploy Sentinel RLS token server
Next we could deploy the Sentinel RLS token server in the K8S cluster.
We’ve provided a deployment template for Sentinel RLS token server in sentinel-rls.yml.
It includes:
- A
ConfigMapthat contains the cluster flow control rule for Envoy global rate limiting. This will be mounted as a file in the targetDeployment, so that the Sentinel RLS token server could load the rules dynamically as soon as the rule in theConfigMaphas been updated. - A
Deploymentfor Sentinel RLS token server. It will mount theConfigMapas a volume for dynamic rule configuration. - A
Servicethat exports the Sentinel command port (8719) and the RLS gRPC port (by default 10245) on a cluster-internal IP so that the Envoy pods could communicate with the RLS server.
The sample rate limiting rule in the sentinel-rule-cm:
domain: foo
descriptors:
# For requests to the "service_httpbin" cluster, limit the max QPS to 1
- resources:
- key: "destination_cluster"
value: "service_httpbin"
count: 1
You may enable the access log in the Sentinel RLS token server (output to console)
via the SENTINEL_RLS_ACCESS_LOG env:
env:
- name: SENTINEL_RLS_ACCESS_LOG
value: "on"
You may also append JVM opts via the JAVA_OPTS env.
After preparing the yaml template, you may deploy the Sentinel RLS token server:
kubectl apply -f sample/k8s/sentinel-rls.yml
Deploy Envoy
Next we could deploy the Envoy instances in the K8S cluster. If you’ve already had Envoy instances running,
you could configure the address (sentinel-rls-service) and the port (10245)
of the rate limit cluster in your Envoy configuration.
We’ve provided a deployment template for Envoy in envoy.yml.
It includes:
- A
ConfigMapthat contains the configuration for Envoy. This will be mounted as a file in the targetDeployment, which will be loaded as the configuration file by Envoy. - A
Deploymentfor Envoy. It will mount theConfigMapas a volume for configuration. - A
Servicethat exports the Envoy endpoint port (by default 10000) on a cluster-internal IP so that it could be accessible from other pods. If you need external access, you could choose theLoadBalancertype or add a frontend ingress.
In the sample, we have two Envoy clusters:
service_httpbin: HTTP proxy tohttpbin.orgrate_limit_cluster: the cluster of the Sentinel RLS token server
This route configuration tells Envoy to route incoming requests to httpbin.org. In the http_filters conf item,
we added the envoy.rate_limit filter to the filter chain so that the global rate limiting is enabled.
We set the rate limit domain as foo, which matches the item in the Envoy RLS rule.
In the route_config, we provide the rate limit action: {destination_cluster: {}}, which will
generate the rate limit descriptor containing the actual target cluster name (e.g. service_httpbin).
Then we could set rate limit rules for each target clusters.
After preparing the yaml template, you may deploy the Envoy instance:
kubectl apply -f sample/k8s/envoy.yml
Test the rate limiting
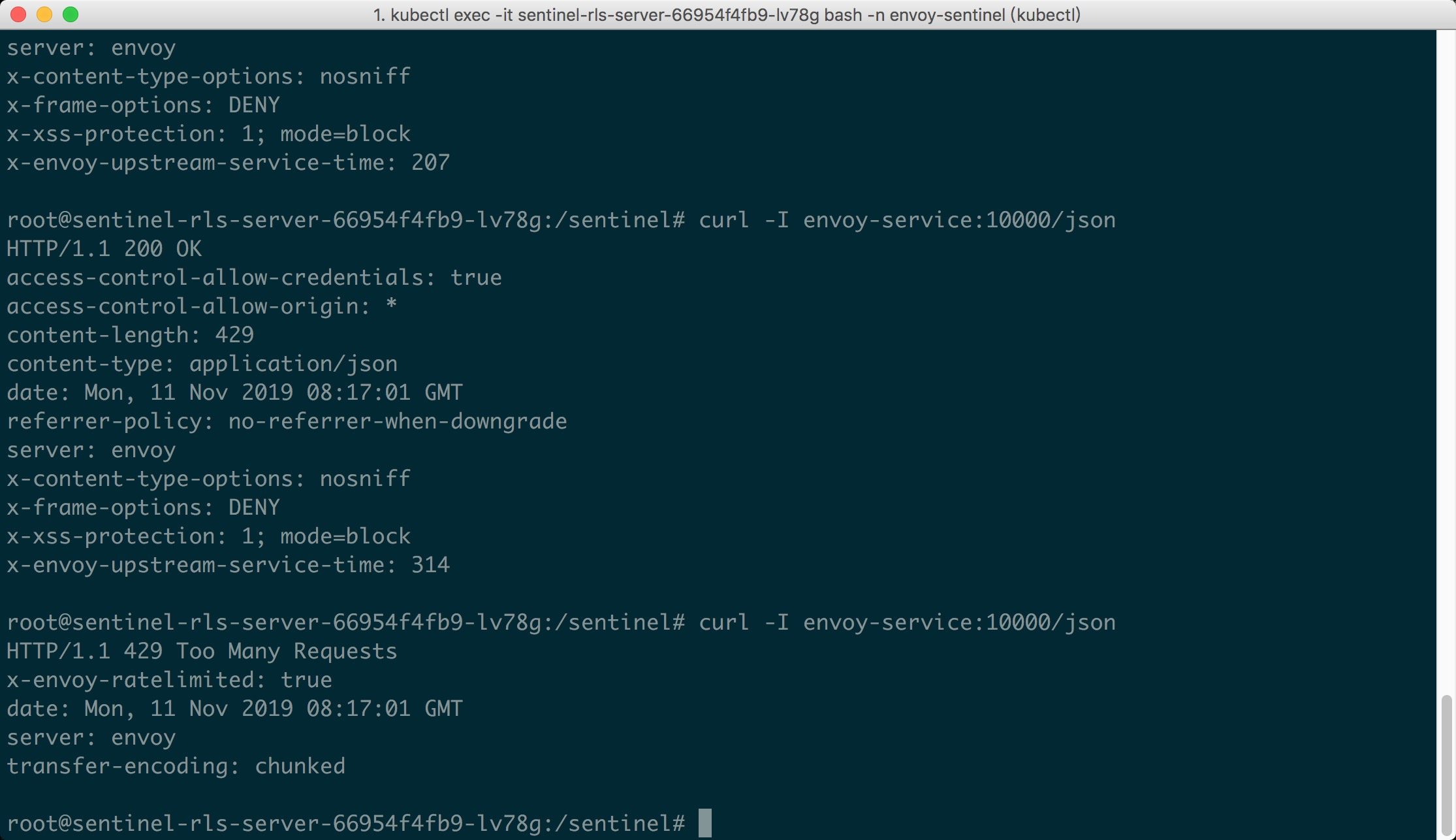
Now it’s show time! We could visit the URL envoy-service:10000/json in K8S pods.
Since we set the max QPS to 1, we could emit concurrent requests to the URL, and we
could see the first request passes, while the latter requests are blocked (status 429):
Update the rules dynamically
You could update the rules in the sentinel-rule-cm ConfigMap. Once the content is updated,
Sentinel will perceive the changes and load the new rules to EnvoyRlsRuleManager.